Learning the Art of Helping Building Blocks and Techniquesã¢ââ by Mark Young

Media Codes and Conventions
Media codes and conventions are similar the building blocks of all the media effectually us. Media codes generally take an agreed pregnant, or connotation, to their audience. There are iii types of media codes, symbolic codes, technical codes and written codes. Conventions are expected ways in which codes are organised in a product.
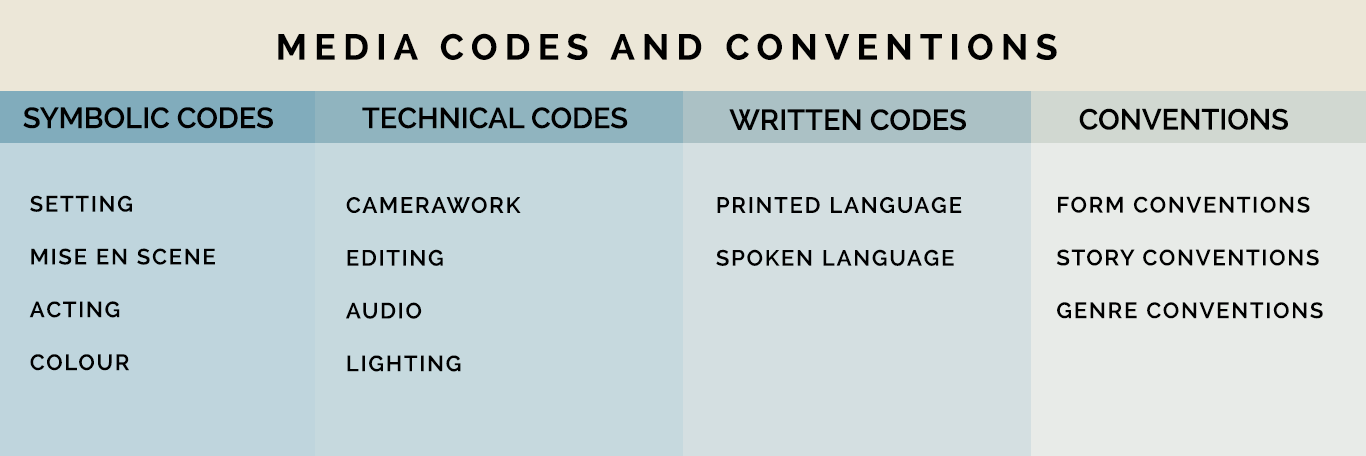

Symbolic Codes
Symbolic codes are social in nature. What this means is that these codes live outside the media product themselves, simply would be understood in similar ways in the 'real life' of the audience. For instance, if you saw somebody receive a red rose in a moving-picture show, you would assume in that location is a romantic relationship between the two characters. If you gave somebody a blood-red rose in real life, yous might be hoping the same. Symbolic codes in media include setting, mise en scene, acting and colour.

Setting
Setting is the fourth dimension and place of the narrative. When discussing setting, you can describe the setting of the whole story or simply a specific scene. A setting can be as big as the outback or space, or as small equally a specific room. Setting can even exist a created temper or frame of mind.

Mise en scene
Mise en scene is a French term that ways 'everything within the frame'. In media terms information technology has get to mean the description of all the objects within a frame of the media product and how they have been arranged. An assay of mise en scene includes:
- Gear up Design
- Costume
- Props
- Staging and Limerick

Acting
Actors portray characters in media products and contribute to character development, creating tension or advancing the narrative. The actor portrays a character through:
- Facial expression
- Body Language
- Vocal qualities
- Move
- Body contact

Color
Colour has highly cultural and stiff connotations. When studying the use of colour in a media production the different aspects to be looking at are:
- Dominant colour
- Contrasting foils
- Colour symbolism

Technical Codes
Technical codes are codes that are specific to a media course and do not live outside of them. For instance, our understanding of dissimilar camera shots and their connotations brand sense when we look and films and photographs, but mean nothing to u.s. outside of those forms. Technical codes in media include Camerawork, Editing, Audio and Lighting.

Camerawork
Camerawork refers to how the camera is operated, positioned and moved for specific effects. Aspects of camerawork include:
- Positioning
- Movement
- Framing
- Exposure
- Lens choice

Editing
Editing is the process of choosing, manipulating and arranging images and audio. Editing is more often than not done for four different reasons:
- Graphic edits
- Rhythmic edits
- Spacial edits
- Temporal edits

Audio
Sound is the expressive or naturalistic employ of audio. Audio can be diegetic or non diegetic. The iii aspects of sound are:
- dialogue
- audio effects
- music

Lighting
Lighting is the manipulation of natural or artificial lite to selectively highlight specific elements of the scene. Elements of lighting include:
- Quality
- Direction
- Source
- Colour

Written Codes
Written codes are the formal written language used in a media product. Just like technical and symbolic codes, written codes can be used to accelerate a narrative, communicate information virtually a character or issues and themes in the media product.
Written codes include printed linguistic communication which is text you lot tin see within the frame and how it is presented, and also spoken linguistic communication, which includes dialogue and song lyrics.

Conventions
Conventions are accepted ways of using media codes. Conventions are closely continued to the audience expectations of a media production. Different types of conventions include form conventions, story conventions and genre conventions.

Form conventions
Form conventions are the certain ways we expect types of media'southward codes to be bundled. For instance an audience expects to have a title of the film at the commencement, and then credits at the finish. Newspapers will have a masthead, the most of import news on the front page and sports news on the back page. Video games usually commencement with a tutorial to explain the mechanics of how the game works.
Another example would be continuity editing. Virtually video forms follow a fix of editing rules and techniques called continuity editing which allows for the audience to easily understand what is going on in a scene and who is talking to who.

Story Conventions
Story conventions are common narrative structures and understandings that are common in story telling media products. Examples of story conventions include:
- Narrative structures
- Cause and effect
- Character structure
- Point of View

Genre Conventions
Genre conventions point to the common employ of tropes, characters, settings or themes in a particular blazon of medium. Genre conventions are closely linked with audience expectations. Genre conventions tin can be formal or thematic.
Learn these codes and conventions through the help of these digital flash cards
Source: https://media.codes/media-codes-and-conventions-c03423c06aa8
0 Response to "Learning the Art of Helping Building Blocks and Techniquesã¢ââ by Mark Young"
Post a Comment